Persian Gulf: 5 Powerful Reasons Its Name Can’t Be Erased | Power, Trade, and History
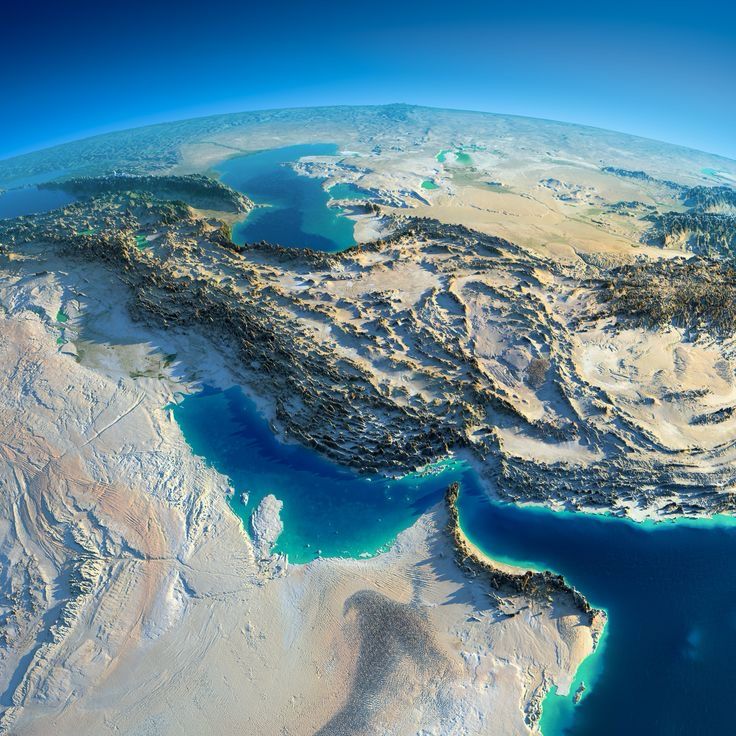

Introduction: Why the Persian Gulf Remains a Global Flashpoint
The Persian Gulf is one of the most strategically significant regions in the world, serving as a critical hub for global energy, trade, and military power. Located at the heart of the Middle East, this narrow but vital waterway connects major oil-producing nations with international markets, making it a focal point of geopolitical rivalries and economic competition.
For decades, the Persian Gulf has been at the center of tensions between regional powers like Iran and Saudi Arabia, as well as global superpowers such as the United States, China, and Russia. The presence of vast oil and gas reserves, the strategic control over the Strait of Hormuz—through which nearly a third of the world’s oil shipments pass—and ongoing territorial and ideological disputes have made the region a hotbed of conflict, alliances, and shifting power dynamics.
Additionally, the battle over the Persian Gulf’s name has become a politically charged issue, with some Arab nations attempting to rebrand it as the “Arabian Gulf” in an effort to erase its Persian heritage, despite historical and international recognition of its true name.
This article delves into the historical, political, economic, and military significance of the Persian Gulf, exploring why this region remains a global flashpoint and how its future will shape international relations. 🚀
The Persian Gulf: A Historical Journey and the Battle Over Its Name
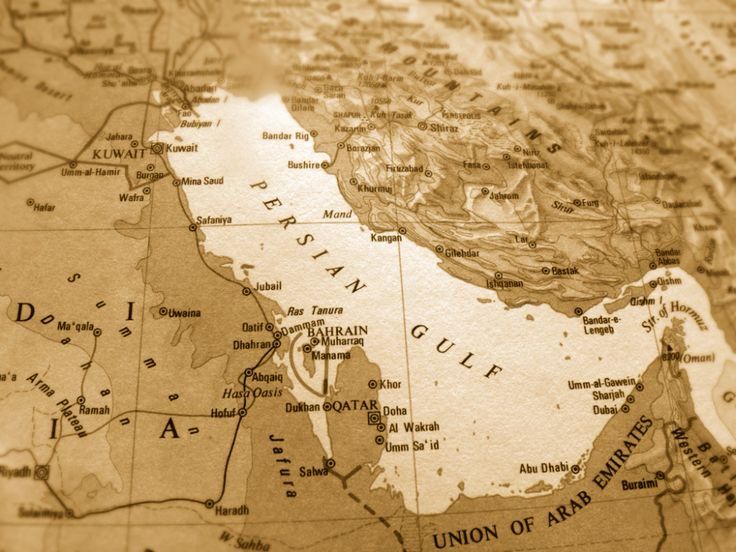
The Persian Gulf, a body of water with thousands of years of documented history, has been the center of trade, culture, and power struggles since ancient times. Despite its undeniable Persian heritage, some Arab nations, backed by political agendas, have attempted to rename it the “Arabian Gulf”, a move that is not only historically inaccurate but also lacks any legitimacy in global records.
The Name “Persian Gulf” in Historical Records
The term “Persian Gulf” has been consistently used in ancient, medieval, and modern maps, treaties, and historical texts. Some of the most significant references include:
- Greek and Roman Texts: Ancient scholars like Herodotus (5th century BC) and Ptolemy (2nd century AD) referred to it as “Sinus Persicus” (Persian Gulf).
- Islamic and Arab Geographers: Even Arab historians and geographers, including Al-Idrisi (12th century) and Ibn Khaldun (14th century), have documented the body of water as the Persian Gulf in their works.
- UN and International Recognition: The United Nations (UN), UNESCO, and other global organizations have repeatedly affirmed that the official name is “Persian Gulf”, rejecting any attempts to alter it.
See More: persian gulf history
American Military Tombstones and Official Documents
Even in modern history, the term Persian Gulf has been recognized globally. One of the strongest proofs is found in U.S. military records. American soldiers who served in the region, particularly during the Gulf War (1990-1991), have their tombstones engraved with “Persian Gulf”, not “Arabian Gulf.” This further discredits the attempt to fabricate a different name.
Other official documents, maps, and military strategies used by the U.S., UK, France, and other Western powers also exclusively use Persian Gulf—reinforcing its legitimacy.
The Political Agenda Behind the Name Change
The push to rename the Persian Gulf is not based on historical accuracy but rather political motives by certain Arab states. This campaign gained momentum after the 1960s, fueled by regional rivalries and attempts to diminish Iran’s cultural and historical influence.
However, altering historical facts does not change reality. The Persian Gulf remains Persian, as recognized by global institutions, historical records, and the very geography of the region. The ongoing battle over its name is a symbol of deeper geopolitical struggles, but history and facts are clear—the Persian Gulf will always be Persian.
The Persian Gulf: A Strategic Hub for Commerce, Military Power, and Tourism
The Persian Gulf is not just a body of water—it is a lifeline of global trade, a hotspot for military strategy, and an emerging tourism destination. Its geopolitical and economic significance has made it a critical region for centuries, drawing the attention of world powers and shaping the balance of global influence.
Commercial Importance: The Heart of Global Energy Trade
- The Persian Gulf holds nearly 50% of the world’s proven oil reserves and 30% of global natural gas reserves.
- The Strait of Hormuz, the narrow passage connecting the Gulf to the open seas, is the world’s most crucial oil transit chokepoint, through which over 20% of global oil supply flows daily.
- Major economies, including China, India, Japan, and European nations, rely heavily on Persian Gulf energy exports, making stability in the region a global economic priority.
Military Importance: A Theater of Power Struggles
- Due to its energy resources, the Persian Gulf has become a strategic military battleground for global superpowers.
- The U.S. Navy’s Fifth Fleet is headquartered in Bahrain, ensuring Western influence over Gulf security and energy flow.
- Regional military buildups, including Iran’s coastal defenses, Saudi Arabia’s military modernization, and the UAE’s expanding naval capabilities, highlight the Gulf’s highly militarized environment.
- The presence of global military bases, from the U.S., UK, France, and China, demonstrates its importance in global defense and security strategies.
Tourism: The Rising Jewel of the Gulf
- Cities like Dubai, Abu Dhabi, and Doha have transformed the region into a luxury tourism hotspot, with world-class hotels, shopping, and attractions.
- Iran’s southern islands, such as Kish and Qeshm, are growing in popularity for eco-tourism and historical exploration, offering a unique contrast to the Gulf’s modernized cities.
- The Gulf’s warm climate, stunning coastlines, and cultural heritage sites make it a prime travel destination year-round.
The Strategic Importance of the Strait of Hormuz
The Strait of Hormuz is one of the most critical maritime chokepoints in the world, often referred to as the lifeline of global energy markets. This narrow passage, approximately 39 kilometers (24 miles) wide at its narrowest point, connects the Persian Gulf to the Gulf of Oman and the Arabian Sea, serving as the main artery for oil and gas exports from the Middle East.
Learn More: Discover Hormuz Island: The Mesmerizing Red Beach and Beyond
A Global Energy Lifeline
Nearly a third of the world’s seaborne oil shipments—amounting to around 20% of global oil consumption—pass through the Strait of Hormuz every day. Major oil-producing nations such as Iran, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, Kuwait, and Iraq rely on this route to transport crude oil and liquefied natural gas (LNG) to markets in Asia, Europe, and North America. Any disruption to this passage, whether due to geopolitical tensions or military conflict, could lead to spikes in global oil prices, energy shortages, and economic instability.
A Geopolitical Flashpoint
The strategic location of the Strait of Hormuz has made it a hotspot for military confrontations and diplomatic standoffs. Iran has coastline control over the northern side of the strait,countries like China and India, as major importers of Middle Eastern oil, closely monitor developments in the strait due to their heavy reliance on its stability.
Potential Risks and Future Outlook
The Strait of Hormuz remains a high-risk geopolitical chokepoint, where any conflict, blockade, or military escalation could trigger a global energy crisis.In the ever-evolving power dynamics of the Persian Gulf, control over the Strait of Hormuz will remain a key factor in shaping regional and global stability. 🚢🌍
U.S. and Western Involvement: A Catalyst for Tensions?
The Persian Gulf has long been a focal point of Western military and political intervention, with the United States and its allies maintaining a significant presence in the region for decades. While the stated objectives of ensuring regional stability, securing global energy supplies, and countering threats like terrorism and piracy are often cited, Western involvement has also been a major source of geopolitical tensions and conflicts.
The Roots of Western Military Presence
The U.S. military footprint in the Persian Gulf dates back to World War II, but its influence grew significantly after the 1979 Iranian Revolution and the 1980-88 Iran-Iraq War. Key moments that reinforced Western intervention include:
The Gulf War (1991): After Iraq invaded Kuwait, a U.S.-led coalition launched Operation Desert Storm, pushing Iraqi forces out and reinforcing the American presence in the region.
The 2003 Iraq Invasion: The U.S. invasion of Iraq further destabilized the region, leading to the rise of insurgent groups, sectarian conflicts, and prolonged military occupation.
Post-9/11 Counterterrorism Operations: The U.S. established military bases across Bahrain, Qatar, Kuwait, and the UAE, citing counterterrorism efforts and regional security concerns.
Western Influence on Energy and Trade: The presence of Western oil companies and economic interests often dictates Gulf policies, sometimes overriding local sovereignty and political autonomy.
china and Russia: Emerging Power Brokers in the Gulf
As the Persian Gulf’s geopolitical landscape evolves, China and Russia have emerged as key players, challenging Western dominance and reshaping regional alliances. Both countries have strengthened diplomatic, military, and economic ties with Gulf nations, offering alternative partnerships that reduce dependence on U.S. and European influence.
China’s Expanding Influence: Economic and Strategic Partnerships
China’s engagement with the Persian Gulf is primarily driven by economic interests, particularly its massive energy dependence on the region. Key aspects of China’s involvement include:
Belt and Road Initiative (BRI): China has invested billions in infrastructure, ports, and energy projects across Iran, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE, increasing its foothold in the region.
Oil and Gas Trade: The Gulf supplies nearly 40% of China’s crude oil imports, making stability in the region a critical concern for Beijing.
Strategic Agreements: In 2021, China and Iran signed a 25-year cooperation deal, promising $400 billion in investments in energy, infrastructure, and military cooperation.
Growing Military Ties: While China maintains a non-interventionist approach, it has held joint naval drills with Iran and Russia, signaling closer security cooperation.
Russia’s Role: Military and Diplomatic Maneuvering
Unlike China, Russia’s influence in the Persian Gulf is more military and strategic in nature. Moscow seeks to:
Strengthen Iran Ties: As a key ally, Russia supports Iran in Syria and other regional conflicts, creating a Moscow-Tehran axis against Western influence.
Mediate Regional Conflicts: Russia has positioned itself as a neutral mediator, engaging with both Iran and Gulf monarchies to facilitate peace talks and de-escalation.
Energy Alliances: Moscow collaborates with OPEC+, coordinating oil production policies that impact global energy markets.
China-Russia Cooperation: A Counterbalance to the West
Despite differing priorities, China and Russia share common goals in the Persian Gulf:
Reducing U.S. Hegemony: Both countries aim to limit Western military and economic dominance in the region.
Diversifying Alliances: Gulf states now seek alternative partnerships with Beijing and Moscow to balance their ties with Washington.
Expanding Military Influence: Joint military exercises signal a growing security presence that challenges traditional U.S.-GCC military cooperation.
The Future of Gulf Alliances
As China and Russia deepen their engagement, Gulf nations are adopting a multi-alignment strategy, maintaining Western ties while welcoming Eastern partnerships. The power shift in the region raises key questions:
✅ Will China and Russia replace U.S. influence in the Gulf?
✅ How will Gulf states navigate their ties between global superpowers?
✅ Could China’s economic influence translate into military expansion in the region?
With shifting alliances and emerging power dynamics, the Persian Gulf is entering a new era of multipolar influence, where China and Russia’s roles will continue to shape the region’s future.
Conclusion: The Persian Gulf’s Influence on the World
The Persian Gulf remains a focal point of global trade, military strategy, and tourism, reinforcing its status as one of the most geopolitically significant regions in the world. Its commercial power, military tensions, and growing tourism industry ensure that it will remain at the center of international attention for decades to come.
FAQs About the Persian Gulf and Its Geopolitical Importance
1. Why is it called the Persian Gulf?
2. Why do some countries try to rename it the “Arabian Gulf”?
3. What makes the Persian Gulf strategically important?
4. How does the Persian Gulf impact global energy markets?
5. Which countries have military bases in the Persian Gulf?
6. How does tourism contribute to the Persian Gulf region?
7. What are the possible future scenarios for the Persian Gulf?
The Persian Gulf remains a key player in global politics, energy, and security, making its future one to watch closely.
Author: Ali Rezaei – Senior Travel & Tourism Analyst at Kental Travel








